The Thyroid Connection to Regular Exercise
페이지 정보

본문
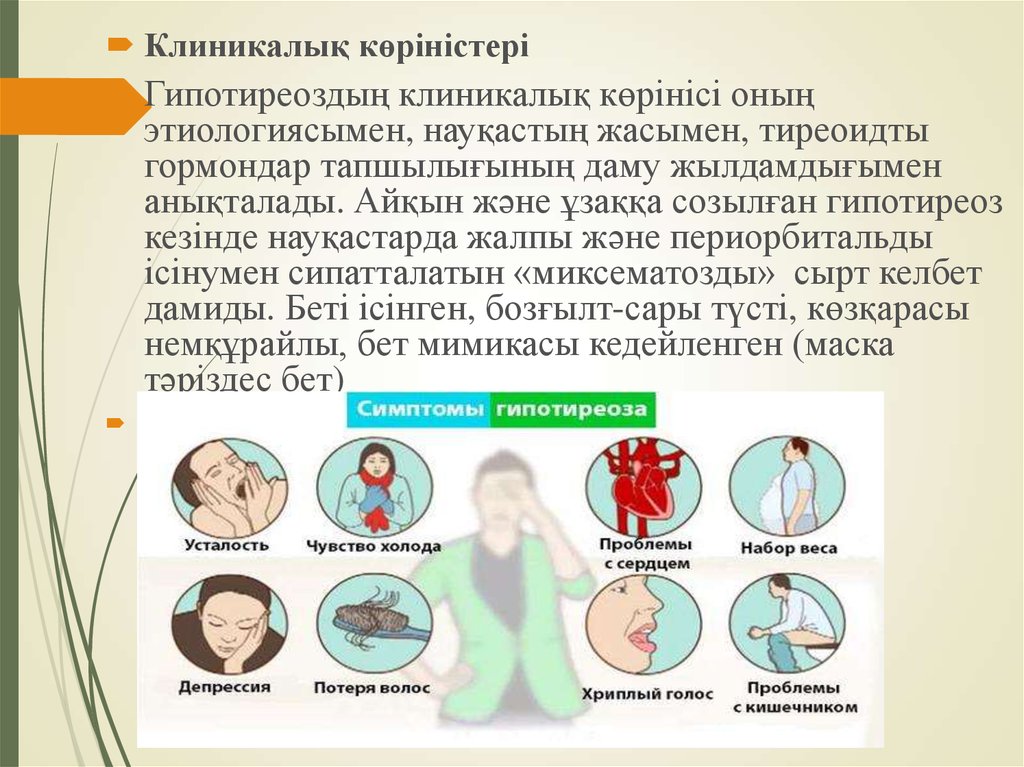
Exercise has become a crucial component of a healthy lifestyle, with numerous benefits for overall physical and mental well-being. While its effects on the body are well-documented, one area where exercise may have a significant impact is on thyroid function. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and growth, with hyperthyroidism, also known as Graves' disease being two common conditions that can arise from thyroid dysfunction.
Thyroid hormones are essential for maintaining optimal metabolic functioning, and they are produced and released by the thyroid gland in response to stimulation from the pituitary gland. When thyroid hormones are produced in excess, hyperthyroidism results, causing an increase in metabolic rate, heart rate, гипертиреоз and energy consumption. Conversely, when thyroid hormones are underproduced, hypothyroidism occurs, leading to decreased metabolic rate, fatigue, and weight gain.
Research has shown that regular exercise can have both positive and negative effects on thyroid function, depending on the type and intensity of exercise, as well as individual factors such as fitness level and health status.
Positive effects of exercise on thyroid function:
- Increased thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) production: TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Physical activity has been shown to increase TSH production, potentially leading to increased thyroid hormone production.
- Enhanced thyroid hormone conversion: Thyroid hormone production involves the conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the biologically active form of the hormone. Exercise has been shown to increase the activity of the enzyme responsible for this conversion, leading to increased production of T3.
- Improved thyroid cancer treatment outcomes: Some studies have suggested that regular exercise may improve treatment outcomes for thyroid growths, possibly by reducing inflammation and improving immune function.
- Increases in cortisol levels: High-intensity exercise can lead to increased production of cortisol, a hormone that can suppress thyroid function.
- Reductions in thyroid hormones: Prolonged or excessive exercise can lead to reductions in thyroid hormone production, potentially exacerbating hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid storm: In rare cases, high-intensity exercise can trigger a thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition characterized by an extreme surge in thyroid hormone production.
- 이전글에리디비지에중계 생성형 AI의 투자 수익률 도난 고용주 25.05.22
- 다음글스프츠라이브중계 이들의 문제 인식 세계 연 매출의 10 25.05.22
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

